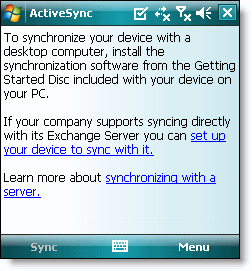
Short for content delivery network, a network of servers that delivers a Web page to a user based on the geographic locations of the user,
the origin of the Web page and a content delivery server. A CDN copies
the pages of a Web site to a network of servers that are dispersed at
geographically different locations, caching the contents of the page.
When a user requests a Web page that is part of a CDN, the CDN will
redirect the request from the originating site’s server to a server in
the CDN that is closest to the user and deliver the cached content. The
CDN will also communicate with the originating server to deliver any
content that has not been previously cached.
This service is effective in speeding the delivery of content of Web sites with high traffic and Web sites that have global reach. The closer the CDN server is to the user geographically, the faster the content will be delivered to the user. CDNs also provide protection from large surges in traffic.
The process of bouncing through a CDN is nearly transparent to the user. The only way a user would know if a CDN has been accessed is if the delivered URL is different than the URL that has been requested.
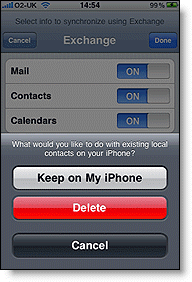
Website without Content Delivery Network (CDN)

Website powered by Content Delivery Network (CDN)

Source: [Webopedia] [Shin] [Ex]
Continue Reading
This service is effective in speeding the delivery of content of Web sites with high traffic and Web sites that have global reach. The closer the CDN server is to the user geographically, the faster the content will be delivered to the user. CDNs also provide protection from large surges in traffic.
The process of bouncing through a CDN is nearly transparent to the user. The only way a user would know if a CDN has been accessed is if the delivered URL is different than the URL that has been requested.
- Faster download: Instead of going all the way to the source, visitors can download website contents stored in the nearest cache server. Cache servers replicate the exact content of the origin server, allowing visitors to download files from the nearest mirror.
- Smoother data transmission: As data travels through a shorter distance, the chance of downloading a deteriorated audio or video file is reduced significantly. You can now provide visitors with high-quality downloadables without compromising speed.
- Load balancing: Overcome network congestion by spreading the traffic over several mirrors. We regard constant website availability as one of the most crucial aspect of your operation. Hence, we will ensure that your website will be able to handle the traffic load at all times.
- Content Redundancy: At times, the immediate server may not be able to function normally due to hardware malfunction or system failure. As CDN exercises content duplication, your website will continue to run smoothly even when our engineers are performing routine maintenance.
- Constant uptime: We recognize the importance of increasing the number of unique visitors as well as encouraging repeated visits to your businesses. Make your website accessible 24/7 by having a backup server that can instantly take over the responsibilities of a faulty server.
- Increased scalability: Expansion is simplified as modifications to website contents are made to only one server. We will gladly support the growth of your website by providing additional mirrors at the time and location of your choice.
- Data integrity: When the source is updated, changes made to it will be copied by all of the cache servers. This enables you to guarantee the consistency of the files and information published.
Entities In Need Of CDN
Business firms, educational institutions and government bodies with offices operating in multiple countries will positively benefit from the implementation of the CDN technology. By reducing the load of the origin server, visitors from all over the world can enjoy the contents and services from your website hassle-free.Website without Content Delivery Network (CDN)

Website powered by Content Delivery Network (CDN)

Source: [Webopedia] [Shin] [Ex]